Boas are an incredibly fascinating group of snakes that have captivated the attention of people for centuries. These animals are known for their impressive size, unique patterns, and incredible strength. But when it comes to identifying different species of boas, things can get a little confusing. One question that often comes up is whether or not all boas are constrictors.
At first glance, it might seem like a simple question to answer. After all, aren’t all boas known for their ability to squeeze their prey to death? But the truth is that there are a number of different species of boas out there, and not all of them rely on constriction to subdue their food. So let’s take a closer look at this question and explore the fascinating world of these amazing snakes.
Yes, all boas are constrictors. Boas are a family of snakes that are characterized by their ability to suffocate their prey by wrapping their bodies around them and squeezing. This method of killing is known as constriction. Boas are found in various habitats around the world and come in a range of sizes, from small sand boas to large anacondas. In addition to their constricting abilities, boas are also known for their beautiful patterns and colors, making them popular pets among reptile enthusiasts.

Are All Boas Constrictors? A Guide to Boa Constrictors and Their Relatives
What Are Boa Constrictors?
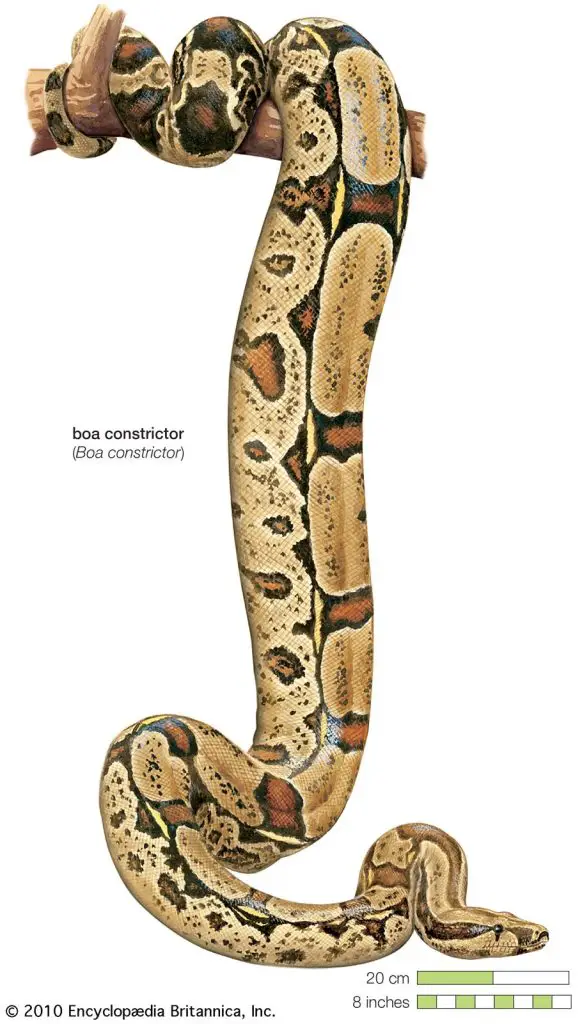
Boa constrictors are large, non-venomous snakes that are found throughout a wide range of habitats in Central and South America. These snakes are known for their distinctive pattern of dark brown or black spots on a lighter background. They are also known for their ability to constrict their prey.
Boa constrictors are members of the Boidae family, which also includes a number of other species of large, non-venomous snakes. Some of the most well-known relatives of the boa constrictor include the anaconda, the python, and the sand boa.
What Are the Differences Between Boa Constrictors and Other Boids?
While boa constrictors and other boids share many similarities, there are also a number of important differences between them. One of the most significant differences is in their size. Boa constrictors are typically smaller than pythons and anacondas, although they can still grow to be quite large. Another important difference is in their habitat. Boa constrictors are found primarily in Central and South America, while pythons and anacondas are found in other parts of the world.
Another difference between boa constrictors and other boids is in their behavior. Boa constrictors are known for being relatively docile and easy to handle, while some species of pythons and anacondas can be more aggressive.
What Are Some Other Species of Boids?
In addition to boa constrictors, there are many other species of boids found around the world. Some of the most well-known species include:
- Green anaconda
- Reticulated python
- Burmese python
- Madagascar ground boa
- Kenyan sand boa
- Rainbow boa
Each of these species has its own unique characteristics and behaviors, but they all share many similarities with the boa constrictor.
Benefits of Keeping Boids as Pets
For many people, keeping boids as pets can be a very rewarding experience. These snakes are intelligent, fascinating creatures that can provide years of enjoyment. They also require relatively simple care, making them a good choice for people who are new to snake ownership.
One of the benefits of keeping boids as pets is that they can help to educate people about these important animals. By learning more about boids and their habitats, people can become more aware of the need to protect these snakes and their ecosystems.
Boa Constrictors vs. Other Popular Pet Snakes
When it comes to choosing a pet snake, there are many options available. Some of the most popular choices include corn snakes, ball pythons, and king snakes. While these snakes can all make great pets, there are some important differences between them and boa constrictors.
One of the biggest differences is in their size. Boa constrictors are much larger than most other popular pet snakes, which can be a consideration for people who have limited space. Another difference is in their temperament. While boa constrictors are generally docile and easy to handle, some other species of snakes can be more aggressive.
How to Care for Boa Constrictors
If you are considering keeping a boa constrictor as a pet, it is important to understand the basics of caring for these snakes. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Provide a large, secure enclosure with plenty of hiding places.
- Keep the enclosure at the appropriate temperature and humidity levels.
- Feed your boa constrictor a diet of appropriately sized prey items.
- Handle your snake gently and regularly to help keep it socialized.
By following these basic care guidelines, you can help ensure that your boa constrictor stays healthy and happy for years to come.
Conclusion
Boa constrictors are fascinating snakes that are beloved by many people around the world. While they share many similarities with other boids, there are also important differences between these species. Whether you are considering keeping a boa constrictor as a pet or simply want to learn more about these amazing animals, understanding their characteristics and behavior can be a great way to appreciate the natural world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are All Boas Constrictors?
Yes, all boas are constrictors. Constrictors are a group of snakes that use their powerful muscles to suffocate their prey by wrapping their bodies around them. Boas are known for their ability to constrict their prey, and this is one of their defining characteristics.
Boas are found in a variety of habitats around the world, including forests, deserts, and wetlands. They come in a range of sizes, from small sand boas to large anacondas. While there are many different species of boa, they all share the common trait of being constrictors.
In addition to their ability to constrict prey, boas are also known for their beautiful patterns and colors. Many boas are kept as pets, and they can make great companions for experienced reptile owners who are willing to provide them with the proper care and attention they need to thrive.
Overall, if you are looking for a snake that is a constrictor, then a boa may be the perfect choice for you. With their powerful muscles and beautiful patterns, these snakes are truly a wonder of the natural world.
How Do Boas Hunt?
Boas are ambush predators, which means that they wait for their prey to come to them. When hunting, boas will typically lie in wait in a strategic location, such as near a burrow or a watering hole.
Once the prey comes within range, the boa will strike, using its powerful muscles to wrap its body around the prey and suffocate it. Boas are able to swallow their prey whole, which allows them to consume animals that are much larger than themselves.
While boas are known for their ability to constrict their prey, they are also opportunistic hunters. This means that they will eat a wide variety of prey, including rodents, birds, and even other snakes.
Overall, boas are formidable hunters that use their strength and cunning to take down their prey. Whether you are a fan of snakes or simply interested in the natural world, these fascinating creatures are sure to captivate your imagination.
What Do Boas Eat?
Boas are carnivorous, which means that they eat meat. They are opportunistic hunters, which means that they will eat a wide variety of prey.
In the wild, boas will eat small mammals, birds, lizards, and even other snakes. Larger species of boas, such as the anaconda, are capable of taking down much larger prey, such as deer and wild pigs.
In captivity, boas are typically fed a diet of rodents, such as mice or rats. It is important to ensure that the prey is an appropriate size for the snake, as feeding a snake prey that is too large can cause health problems.
Overall, boas are versatile hunters that are able to adapt to a wide variety of prey. Whether in the wild or in captivity, these snakes are able to thrive on a diet of meat.
How Big Do Boas Get?
Boas are a diverse group of snakes that come in a range of sizes. The smallest species of boa, the sand boa, grows to be only a few feet long.
The largest species of boa, the green anaconda, can grow to be over 20 feet long and weigh over 200 pounds. However, most species of boa fall somewhere in between these two extremes.
The size of a boa will depend on a variety of factors, including its species, age, and diet. In captivity, boas can be kept at a smaller size by feeding them a diet of appropriately sized prey.
Overall, boas are a fascinating group of snakes that come in a variety of sizes. Whether you are interested in small sand boas or giant anacondas, there is a boa out there for everyone.
Are Boas Dangerous?
Boas are generally not considered to be dangerous to humans. While they are capable of constricting their prey, they are not venomous and do not pose a significant threat to humans.
However, it is important to remember that boas are wild animals and should be treated with respect. Even a non-venomous snake can bite if it feels threatened or cornered.
If you are considering keeping a boa as a pet, it is important to research the species thoroughly and ensure that you are able to provide it with the proper care and attention it needs to thrive. With the proper precautions and care, boas can make great pets for experienced reptile owners.
Overall, while boas are not typically considered to be dangerous, it is still important to treat them with respect and caution. By doing so, you can enjoy these fascinating creatures without putting yourself or others at risk.
Boa Constrictor Care Guide 2022 | Everything You Need To Know!
In conclusion, not all snakes that are commonly referred to as “boas” are actually constrictors. While most boas are indeed constrictors, there are a few exceptions, such as the sand boa and the rosy boa.
It’s important to note that the term “boa” is often used colloquially to refer to any snake that’s large and heavy-bodied. However, from a scientific standpoint, the term only refers to members of the Boidae family.
Regardless of whether or not a snake is a constrictor, it’s always important to handle them with care and respect. These fascinating creatures play important roles in their ecosystems, and with the right knowledge and precautions, they can be enjoyed safely by humans as well.