Have you ever wondered if alligators have ears? You’re not alone! Despite their intimidating appearance and reputation, there is still much to be learned about these prehistoric creatures.
While alligators may not have visible ears like humans do, they do in fact have an auditory system that allows them to hear sounds both above and below water. So, let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of alligator anatomy and explore the amazing adaptations that have allowed them to survive for millions of years.
Yes, alligators have ears, but they are not visible from the outside. They have small openings on either side of their heads that lead to internal ear structures. These structures allow them to hear both in water and on land.

Do Alligators Have Ears?
Alligators are fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years. They are known for their powerful jaws, scaly skin, and impressive size. But do alligators have ears? The answer may surprise you.
Yes, Alligators Have Ears
Contrary to popular belief, alligators do have ears. However, their ears are not visible from the outside like human ears. Instead, they have small openings on the sides of their heads that lead to their inner ears. These openings are covered by flaps of skin that protect them from water and debris.
Alligators have excellent hearing, which is crucial for their survival. They use their ears to detect sounds in the water and on land, including the calls of other alligators, the movements of prey, and the approach of predators. In fact, alligators can hear sounds from a distance of up to 200 yards.
If you’re wondering why alligators don’t have external ears like humans, it’s because they don’t need them. Alligators have evolved to thrive in their environment, and their unique ear structure is just one of the many adaptations that help them survive.
How Alligators Hear
Alligators hear differently than humans do. While we hear through our eardrums, alligators use something called a “cochlear duct” to hear. This duct is a long, fluid-filled tube that runs through the alligator’s inner ear. When sound waves enter the ear canal, they cause vibrations that travel through the fluid in the cochlear duct, stimulating tiny sensory cells called hair cells. The hair cells then send electrical signals to the brain, which interprets them as sound.
Alligators are particularly sensitive to low-frequency sounds, which is why their calls and grunts are often deep and resonate through the water. In fact, alligators can communicate with each other through a range of sounds, from low-frequency rumbles to high-pitched hisses.
The Benefits of Alligator Ears
Alligator ears are an essential part of their survival. They help alligators detect prey, avoid predators, and communicate with each other. By hearing the sounds of their environment, alligators can also navigate through their habitat more easily and find suitable nesting sites.
In addition to their impressive hearing, alligators have other adaptations that make them formidable predators. Their sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and muscular tails allow them to catch and kill prey with ease. They can also hold their breath for long periods of time, which helps them stay hidden from predators and stalk their prey.
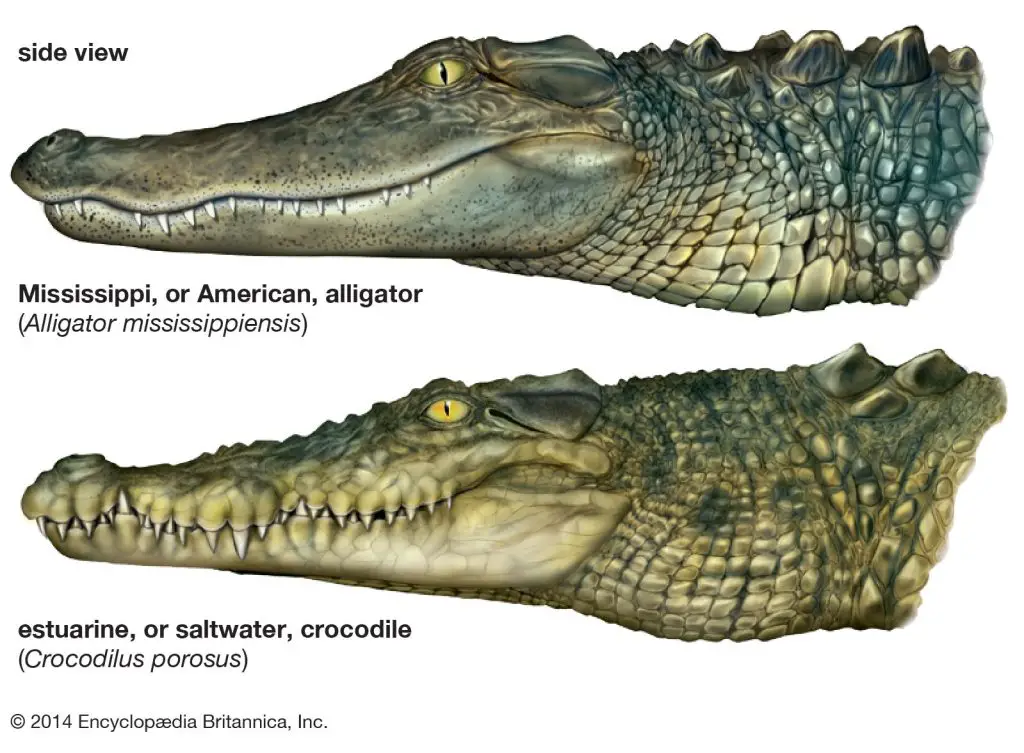
Alligators vs. Crocodiles
If you’re wondering if crocodiles have ears, the answer is yes. Crocodiles have a similar ear structure to alligators, with small openings on the sides of their heads that lead to their inner ears. However, there are some differences between alligators and crocodiles.
One of the biggest differences between alligators and crocodiles is their snouts. Alligators have wide, rounded snouts, while crocodiles have longer, more pointed snouts. This difference affects their hunting habits, with alligators preferring to hunt in shallow water and crocodiles being more versatile hunters.
Additionally, alligators are found exclusively in the Americas, while crocodiles are found all over the world. There are also differences in their behavior and vocalizations, with alligators being more vocal and social than crocodiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alligators do have ears, but they are not visible from the outside. Their unique ear structure allows them to hear sounds in their environment and communicate with each other. Alligators are fascinating creatures that have adapted to their environment in many ways, including their impressive hearing. If you ever have the chance to observe alligators in the wild, take the time to appreciate the many adaptations that make them such successful predators.
| Alligators | Crocodiles |
|---|---|
| Wide, rounded snouts | Long, pointed snouts |
| Found in the Americas | Found all over the world |
| More vocal and social | Less vocal and social |
- Alligators have excellent hearing.
- Alligators use their ears to detect sounds in the water and on land.
- Alligators have a unique ear structure that allows them to hear through a cochlear duct.
- Alligators are particularly sensitive to low-frequency sounds.
- Alligator ears are an essential part of their survival.
- Crocodiles have a similar ear structure to alligators.
- Crocodiles have longer, more pointed snouts than alligators.
- Alligators are found exclusively in the Americas.
- Crocodiles are found all over the world.
- Alligators are more vocal and social than crocodiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the anatomy of an alligator’s ear?
Alligators have ears that are located behind their eyes. They are covered by a flap of skin and are not visible from the outside. The ears are connected to the mouth by a small canal which helps them to hear even when they are underwater.
The alligator’s ears are also equipped with special muscles that allow them to close their ears when they are submerged. This helps to protect their ears from damage and also allows them to hear better by blocking out external noise.
How do alligators hear?
Alligators have a very sensitive hearing that allows them to detect sounds both above and below the water. They can hear frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 1 kHz. They use their ears to locate prey, communicate with other alligators, and detect potential predators.
When an alligator hears a sound, it can pinpoint the location of the source by tilting its head and changing the position of its ears. This allows it to accurately locate prey and avoid danger.
Can alligators hear well?
Yes, alligators have excellent hearing. Their ears are designed to detect sounds both above and below the water, and they can hear frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 1 kHz. They use their hearing to locate prey, communicate with other alligators, and detect potential predators.
Alligators have a very sensitive hearing that allows them to detect even the slightest vibrations in the water. This helps them to locate prey even in murky water where visibility is limited.
How do alligators communicate with each other?
Alligators use a variety of sounds to communicate with each other, including hisses, grunts, and bellowing. They also use body language, such as tail slapping and head nodding, to convey messages.
Alligator communication is especially important during the breeding season when males compete for females. Male alligators will bellow to establish their territory and attract females. They will also use body language to intimidate rival males and protect their territory.
Do alligators have a sense of hearing?
Yes, alligators have a highly developed sense of hearing. Their ears are designed to detect sounds both above and below the water, and they can hear frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 1 kHz. They use their hearing to locate prey, communicate with other alligators, and detect potential predators.
Alligators also have the ability to close their ears when they are submerged, which helps to protect them from damage and allows them to hear better by blocking out external noise. Their hearing is especially important for hunting and avoiding danger in their aquatic environment.
Cool Alligator Facts- Featuring Rex! (My Alligator)
In conclusion, the answer is yes – alligators do indeed have ears! Despite their reputation as fierce and dangerous predators, alligators are fascinating animals that possess a variety of unique physical characteristics. Their ears are located on the sides of their heads, and while they may not be immediately visible, they play an important role in the alligator’s ability to sense its environment.
Interestingly, alligator ears are not just used for hearing. They also play a role in the animal’s communication and social interactions. Alligators are known to make a variety of vocalizations, from hissing and growling to bellowing. These sounds are used to establish territory, attract mates, and communicate with other alligators in their group.
Overall, learning about the unique features of alligators can be both educational and entertaining. While they may not be the cuddliest creatures around, they are certainly fascinating to study and observe. So the next time you see an alligator, remember that it has ears just like you do – and who knows what other surprises it might have in store!