Rattlesnakes are infamous for their venomous bite, which can be deadly to humans and animals alike. But have you ever wondered how these serpents kill their prey? It’s a fascinating process that involves a combination of stealth, precision, and deadly venom.
Rattlesnakes use their venom to immobilize and kill their prey, which can range from rodents to birds to other snakes. However, it’s not just the venom that does the job – rattlesnakes also use their powerful jaws and muscular bodies to constrict and suffocate their victims. Let’s take a closer look at how rattlesnakes hunt and kill, and what makes them such effective predators.
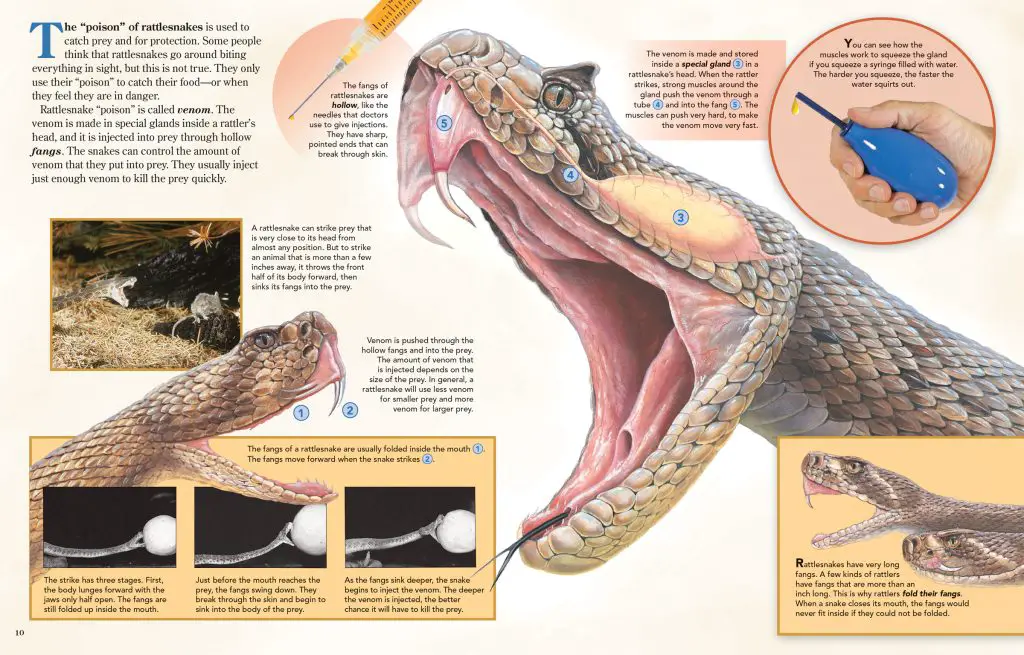
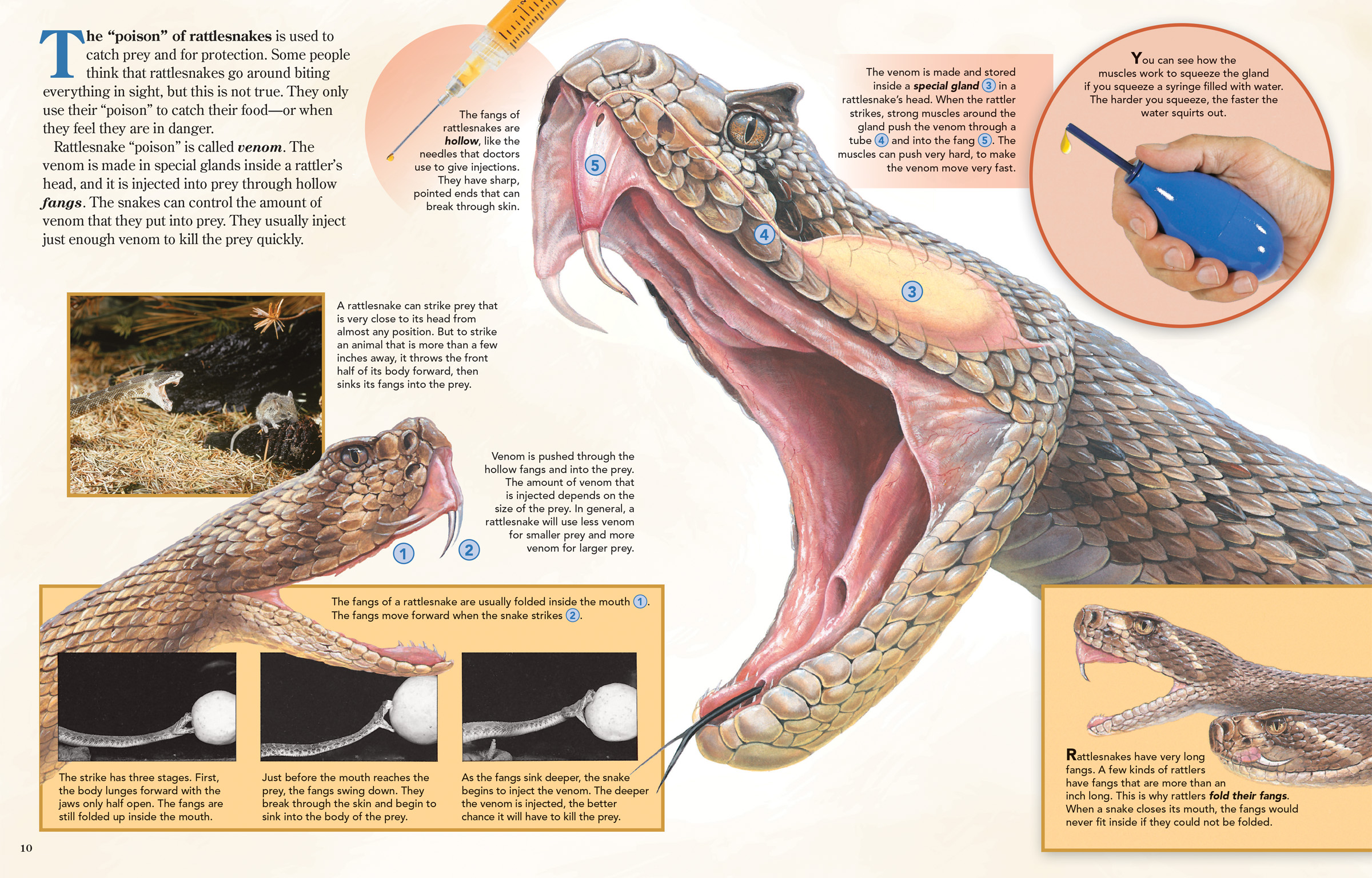
Rattlesnakes kill their prey by injecting venom through their fangs. Once the prey is bitten, the venom quickly spreads through the bloodstream and causes paralysis. The snake then uses its powerful muscles to constrict the prey, suffocating it to death.
How Do Rattlesnakes Kill Their Prey?
Rattlesnakes are one of the most feared and strikingly beautiful creatures in the animal kingdom. They are known for their unique ability to kill their prey with a single venomous bite. But have you ever wondered how rattlesnakes kill their prey? In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of rattlesnakes and their predatory tactics.
Anatomy of a Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that belong to the Viperidae family. They have long, slender bodies that can range in length from one to eight feet. Their heads are triangular in shape and are distinct from their bodies. Rattlesnakes’ eyes are located on the sides of their heads, and they have heat-detecting pits on their faces that help them locate prey.
Rattlesnakes have long, hollow fangs that are used to inject venom into their prey. These fangs are located in the front of their mouths and can be up to two inches long. Rattlesnakes are also equipped with an extraordinary sense of smell, which helps them locate prey even in complete darkness.
Hunting Techniques of Rattlesnakes
Rattlesnakes are ambush predators, which means they wait for their prey to come to them. They often hide in the shadows or under rocks and wait for unsuspecting prey to come within striking distance. Once a prey item is within reach, the rattlesnake will strike with lightning speed and inject venom into its victim.
Rattlesnakes are also known to use their rattles to lure prey. The rattling sound mimics the sound of a cicada or grasshopper, which attracts prey to investigate the source of the sound. When the prey gets close enough, the rattlesnake strikes and delivers a fatal bite.
Venom of Rattlesnakes
The venom of rattlesnakes is a potent cocktail of enzymes and toxins that can cause a range of symptoms in their prey. The venom can cause tissue damage, paralysis, and even death. Rattlesnakes use their venom to immobilize their prey, making it easier to consume.
The venom of rattlesnakes is also used for self-defense. When threatened, a rattlesnake will coil up and rattle its tail to warn predators to stay away. If the predator does not heed the warning, the rattlesnake will strike and deliver a venomous bite.
Digestion of Prey
After a rattlesnake has killed its prey, it will swallow it whole. Rattlesnakes have extremely stretchy jaws that allow them to swallow prey items that are much larger than their heads. Once the prey is swallowed, the rattlesnake’s digestive system goes to work.
Rattlesnakes have a very slow metabolism, which means they can go weeks or even months without eating. The digestive process can take several days to complete, during which time the rattlesnake will rest and conserve energy.
Benefits of Rattlesnakes
While rattlesnakes may seem like a dangerous and scary creature, they play an important role in the ecosystem. Rattlesnakes help to control the population of rodents and other small animals that can be destructive to crops and gardens. In addition, rattlesnakes are a vital part of the food chain and provide food for other predators such as hawks and eagles.
Rattlesnakes vs. Humans
While rattlesnakes are generally not aggressive towards humans, they can be dangerous if provoked or cornered. If you encounter a rattlesnake in the wild, the best course of action is to give it plenty of space and allow it to move away on its own. If you are bitten by a rattlesnake, seek medical attention immediately.
In conclusion, rattlesnakes are fascinating creatures that use unique predatory tactics to hunt and kill their prey. While they may be feared by many, they play an important role in the ecosystem and should be respected from a safe distance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the hunting strategy of rattlesnakes?
Rattlesnakes are ambush hunters. They stay still and wait for their prey to come within striking distance. They have excellent camouflage abilities and can remain invisible to their prey until the last moment. Once the prey is within range, the rattlesnake strikes with lightning speed, injecting venom into the prey’s body.
The venom paralyzes the prey and also begins the process of digestion. The rattlesnake then waits for the prey to die before consuming it.
What kind of venom do rattlesnakes have?
Rattlesnakes have hemotoxic venom, which means it attacks the circulatory system of the prey. The venom causes blood vessels to break down, leading to internal bleeding and tissue damage. It also lowers blood pressure, which can cause shock and even death in the prey.
The venom of rattlesnakes varies in potency depending on the species and individual snake. Some rattlesnakes have venom that is more toxic than others.
How does the rattle of the rattlesnake help it in hunting?
The rattle of the rattlesnake is made up of a series of hollow segments, which vibrate when the snake moves. This creates a distinctive rattling sound that warns potential threats of the snake’s presence.
However, the rattling sound also serves another purpose in hunting. It can lure prey towards the snake. Small mammals like rodents and rabbits are curious and may investigate the sound, leading them right into the strike zone of the rattlesnake.
What happens if a rattlesnake misses its strike?
Rattlesnakes are incredibly accurate hunters, but they do miss their strikes occasionally. If a rattlesnake misses its strike, it will usually retreat and wait for its venom to replenish before trying again.
If the prey manages to escape, the rattlesnake will not pursue it. It takes a lot of energy for a rattlesnake to hunt and strike, and pursuing a prey that has escaped is not worth the effort.
Can rattlesnakes kill humans?
Rattlesnakes can be deadly to humans if they inject a sufficient amount of venom. However, fatalities from rattlesnake bites are rare in the United States. Most bites occur when people accidentally step on or disturb a rattlesnake.
If you encounter a rattlesnake, it is best to stay away and give it plenty of space. If you are bitten, seek medical attention immediately. Anti-venom is available and can be very effective in treating rattlesnake bites.
Snakes on the hunt, venomous King cobra, rattlesnake, pit viper, Gaboon viper, Grass and Dice snake
In conclusion, rattlesnakes are fascinating creatures with unique hunting capabilities. Their venomous bite not only immobilizes their prey but also begins the process of digestion. This allows them to consume their prey whole and obtain all the necessary nutrients.
While their venom is deadly to their prey, it is also a critical tool for their survival. Rattlesnakes use their venom to defend themselves against predators and to compete with other snakes for resources.
Overall, the way rattlesnakes kill their prey is a testament to their adaptability and evolution. As we continue to learn more about these remarkable creatures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the natural world.